Last Updated on 05/12/2023 by Dolly
In the complex world of cybersecurity, zero-day vulnerabilities are always a challenge. Since the flaws in the software are not known to the vendor, there are no patches or fixes available. Cybercriminals take advantage of this and organize attacks and create threats on a small and large scale, from individuals to nations. This article discusses how zero-day vulnerabilities are discovered, how they are exploited, and important measures to mitigate their impact on virtual security.
Discovery of Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
1. Independent Researchers
Ethical hackers (White Hat) and independent security researchers often discover zero-day vulnerabilities through extensive code analysis and security testing. They report their findings to the software vendor for remediation.
2. Security Communities
Online security communities and forums provide a platform for researchers to collaborate and share their discoveries. These collective efforts often lead to the detection of previously unknown vulnerabilities.
3. Nation-Stake Actors
Nation-state intelligence agencies spend significant resources to identify and stockpile zero-day vulnerabilities. These agencies can use these vulnerabilities for cyber espionage or offensive purposes.
Exploitation of Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities is the use of unknown or unpatched security flaws in software, hardware, or firmware to gain unauthorized access to a system or network. Zero-day vulnerabilities are particularly dangerous because they can be exploited before security vendors are aware of them and have a chance to release a patch.
1. Targeted Attacks
State-sponsored hackers and cybercriminals use zero-day vulnerabilities in highly targeted attacks against specific individuals, corporations, or nations. These attacks are usually well-crafted and difficult to detect.
2. Malware and Ransomware
The underground market for cybercriminals is flooded with zero-day vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities are exploited by malware writers and ransomware developers to increase the effectiveness and impact of their malicious software.
3. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
APT groups are often associated with nation-state actors. In covert operations, they use zero-day vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to sensitive systems and data.
Mitigating the Impact of Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
1. Patching and Updating
It is necessary to regularly update software and operating systems to ensure that previously known vulnerabilities are patched. While patches do not prevent zero-day vulnerabilities, they do provide protection from general attacks.
2. Network Segmentation
Network segmentation should be used to limit lateral movement within networks. This way, if one segment is compromised, the rest of the network remains inaccessible to the attacker.
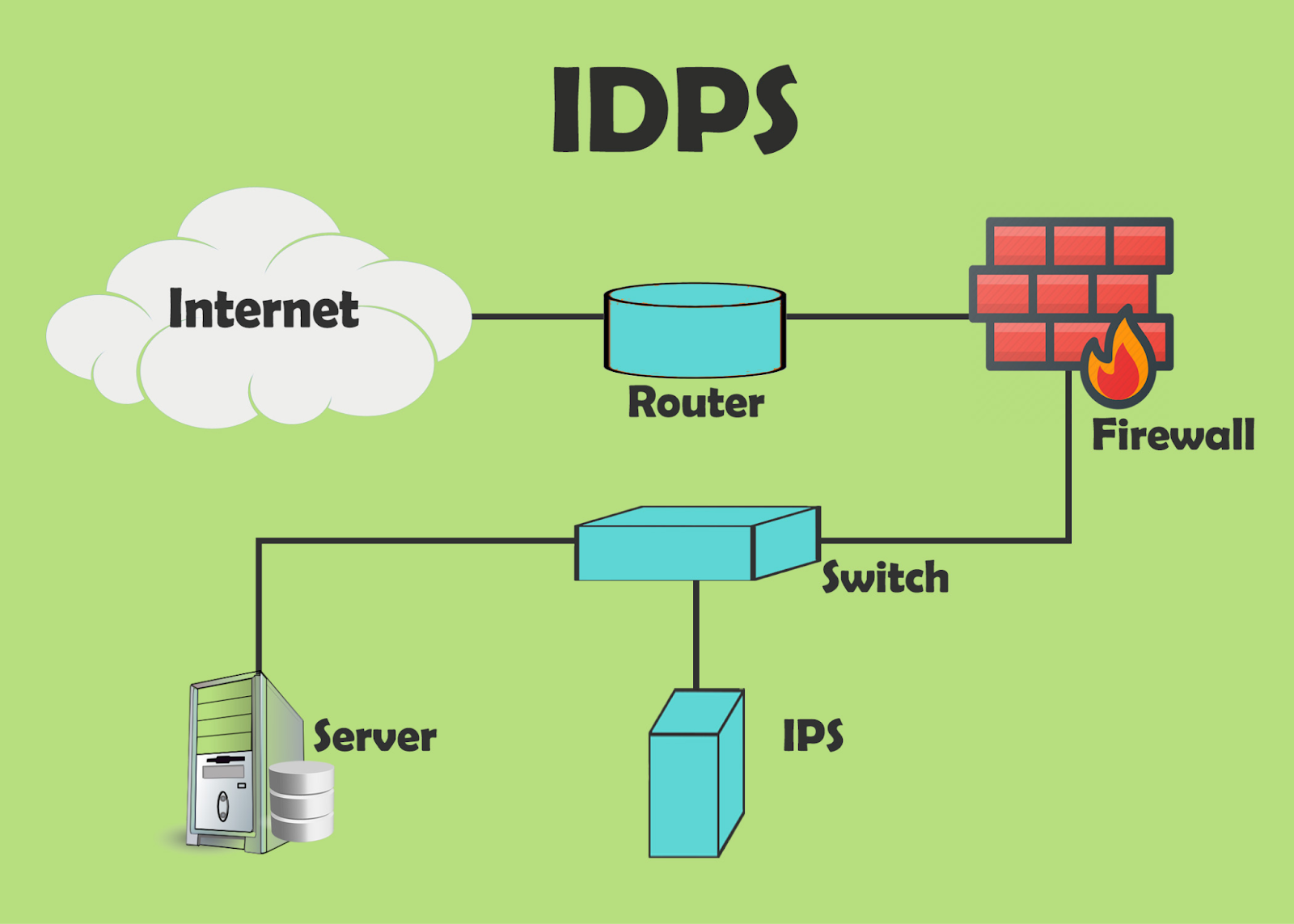
3. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
IDPS deployment should be used to block suspicious activity and behavior within the network. Advanced IDPS solutions can identify and mitigate zero-day attacks in real-time.
 4. User Education and Awareness
4. User Education and Awareness
Recognizing phishing attempts, avoiding suspicious downloads, and educating users on safe browsing habits are essential. Users are often the first line of defense against zero-day exploits.
5. Behavioral Analysis
Leveraging behavioral analytics tools is ideal for monitoring apps and user behavior. Anomalies in application behavior can indicate potential abuse attempts and allow for timely intervention.
6. Collaborate with Cybersecurity Communities
Engage with cybersecurity communities and share threat intelligence. Collaborative efforts increase awareness and preparedness against emerging threats, including zero-day vulnerabilities.
Zero-day vulnerabilities pose a difficult problem in the rapidly evolving field of cybersecurity. Although finding and exploiting these vulnerabilities is a difficult process, their impact can be minimized by putting in place strong security measures and encouraging cooperation within the cybersecurity community. By remaining vigilant, continuously updating systems, and investing in advanced security solutions, individuals and organizations can significantly increase their resilience against these powerful cyber threats.
Read More:
- How to Defend Against Ransomware Attacks in 2023
- The Role of AI in Financial Services: From Robo-Advisors to Fraud Detection
- The Importance of Explainable AI (XAI) in Understanding Intelligent Systems